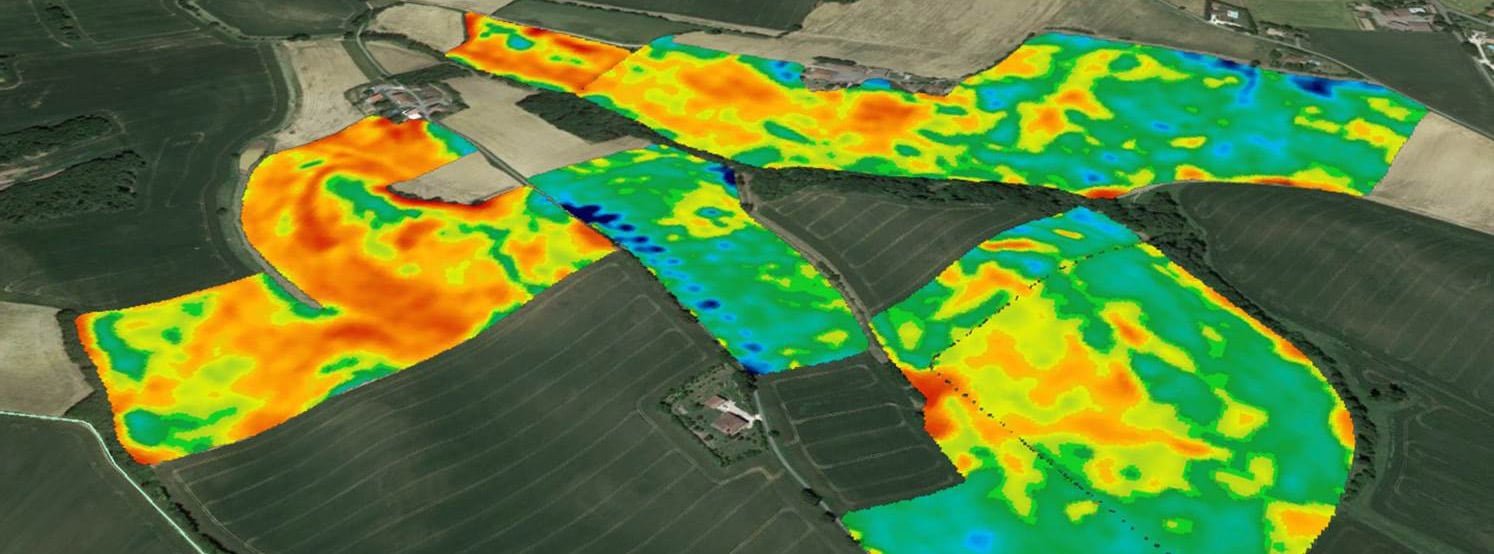
Our specifics
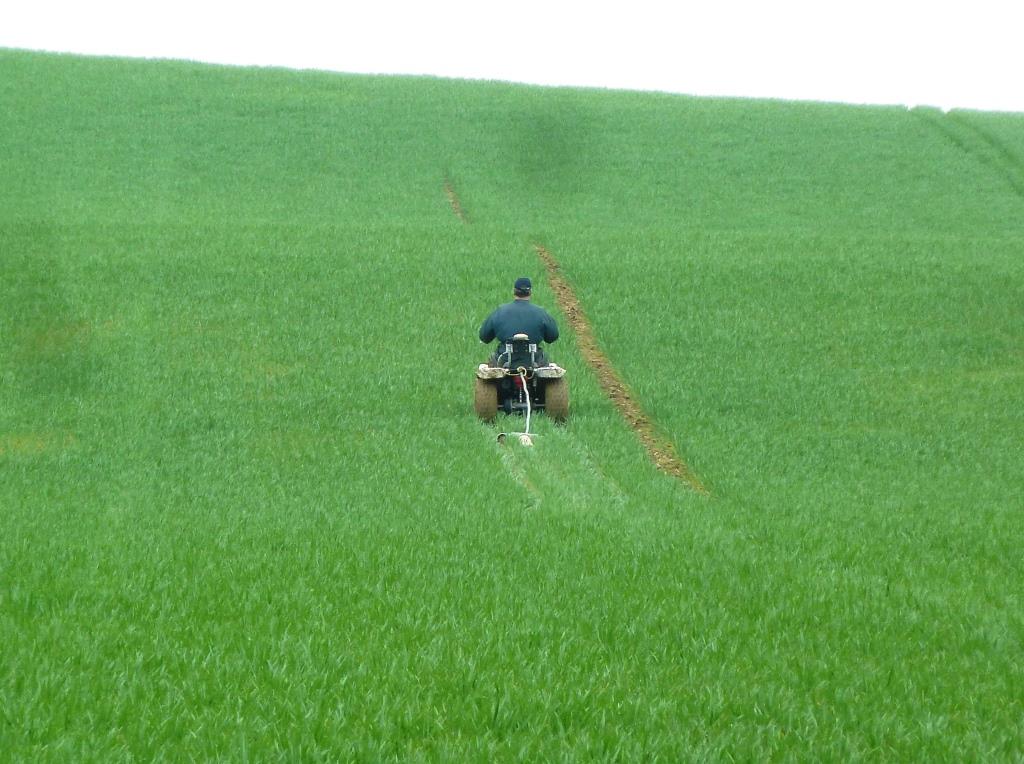
CoRHIZE operates with its own measurement and recording equipment
- a lightweight, non-destructive rolling set, allowing passages on bare soil, on recent seedlings, or on young crops without any damage, on any type of soil, even low lift

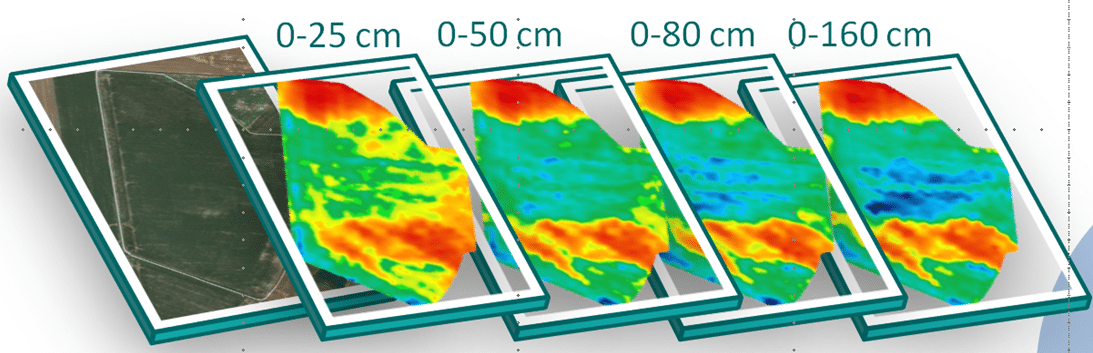
- a patented technology of Canadian geophysics specialist DualEMmeasuring 4 depths simultaneously for better vision of horizons colonized by roots (0-25cm, 0-50cm, 0-80cm, 0-160cm). The segmentation of the two horizons 0-25 cm and 0-50 cm is all the more relevant as these are the horizons most explored by the roots.
- very high resolution of continuously recorded measurements and centimetric GPS positions
A restitution of maps according to the purposes
- raw mapping of the 4 depths, centimetre mapping of gradients and % of slopes, paper documents or computer files in formats compatible with any Agricultural or General Geographic Information System, or modern parcel software
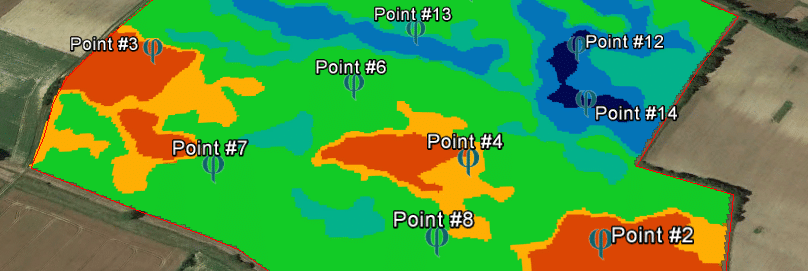
- zoning for soil sampling and/or surveys to carry out fertility and potential mappings
- zoning to qualify the differences of Useful Reserve, help in the definition of homogeneous irrigation areas and the positioning of probes for irrigation management which is a central competence of CoRHIZE
Le support CoRHIZE
- with farmers or their technical advisors for compiling multi-source mapping (soil, yield, TV and proxi detection…), statistical treatments and agronomic analyses for modulated intake requirements
- experimental services (institutes, seed companies, chemists, appros distributors…) in the analysis of yield or qualitative value results compared to soil variability in test plots, spatialization of the variability of the Water Useful Reserve and recommendation of optimized positioning of probes for irrigation, in programming for Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) for water inputs modulated by sectors or microzones
- Free online access for all users who are not equipped with a GIS, the Precision Cropping Technologies Pty Ltd computer solution specific for Precision Agriculture, and of which CoRHIZE is the authorized distributor
- Storing data on a secure server that is accessible at any time by simply connecting or pooling local and remote directories.
- all the experience of CoRHIZE independent company specializing in control and decision support services and tools for Agriculture and Precision Irrigation

Why measure intraparcellary variability?
Intraparcellary variability reflects the heterogeneity of one or more parameters within the same plot. These differences in environment (texture, fertility, pH, RFU, salting…) performance (biomass, efficiency, quality, etc.) need to be studied to act separately and to derive the best technical and economic potential from each square metre of the parcel. This is the ultimate goal of Precision Agriculture, to bring what is needed, where it is needed and when it is needed.
In this sense, soil mapping is the starting point of Precision Agriculture because it focuses on the only ground parameter without interference from others.
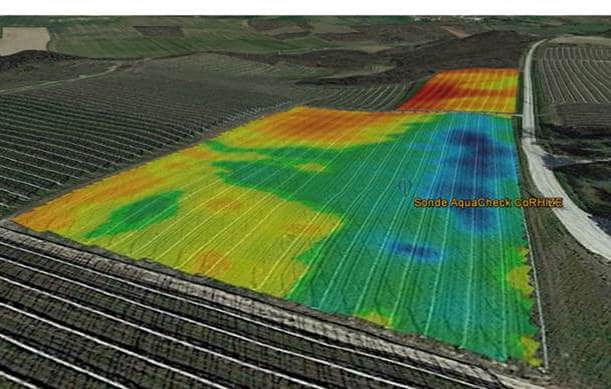
Soil quality is the first factor influencing performance. Soil Conductivity mapping has multiple applications for:
- Precision Agriculture:
- modulation of seedling densities
- modulation and optimization of fertilization
- choice of varieties, rootstocks, …
- Precision Irrigation:
- positioning of profile capacitive probes in areas most relevant to irrigation control
- sizing irrigation equipment
- variable rate irrigation VRI of winders, pivots and ramps
- Experimentation:
- validation of test plots
- multiplying the power of statistical results
- overlaying and cross-referencing multi-resource data (yield, NDVI…)
- Qualitative Harvests:
- selective harvesting
- alloted cereal crops
NOTE: If vegetation mapping is carried out by satellites or drones, soil mapping over several depths cannot be carried out ONLY by specific measurement tools dragged to the ground.
Video
Watch the video on our ground mapping service.
Is it absolutely necessary to use automated modulation tools to use soil mapping?
Soil mapping has multiple applications. If its optimization requires automated modulation tools (fertilizer spreader with on-board weighing and modulation, seeders with density modulation, pivots with dose modulation…), these are not obligatory to start valuing soil mapping.
Soil mapping brings above all a better knowledge of the agronomic potentials of its plots. By bringing them closer to field observations, to history, it allows to ask the right questions and generally to provide the right answers. The then implementation of patches can be done either in manual modulation, although not practical; either by providers or Cumas that are equipped with tools with automated modulation if the farmer is not equipped with them himself. The lack of automated modulation tools on the operation should not be a hindrance to improving the knowledge of its soil.